Staphylococcus aureus diseases are caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It’s a gram-positive bacteria that appear in clusters and are non-motile cocci.
They are usually found on the skin and the respiratory tract of the human body. It is usually written as S. aureus or Staph aureus in a medical context.
This bacteria causes a lot of infections and it’s majorly known as one of the five most common causes of infections.
They’re also known to be antimicrobial resistant due to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Here’s the ultimate list of the diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus aureus diseases
- Food poisoning/diarrhea
- Abscess and sycosis
- Boils (furuncles and carbuncles)
- Cellulitis
- Folliculitis
- Impetigo
- Ecthyma
- Folliculitis decalvans
- Dermatitis
- Erysipelas Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Staphylococcal scarlatina
- Bacteremia
- Pneumonia
- Endocarditis
- Bacteriuria
- Meningitis
- Keratitis
- Endophthalmitis
- Blepharitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Dacryocystitis
- Osteomyelitis
- Swimmer’s ear
- Septicemia
- Mastitis
- Sinusitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Pharyngitis
- Surgical site infections
- Type 2 diabetes
- Paronychia
Staphylococcal food poisoning or intestinal infection

Toxins are produced by Staphylococcus aureus, and these are responsible for gastrointestinal illnesses like food poisoning.
These toxins are usually found in food that is not cooked or is not properly stored. Sliced meats, milk, and cheese, for instance, are good mediums for this contamination.
The fact that toxins can be harmful or not is quite frightening. This means that toxins are not destroyed with heat and will persist in causing illness.
Stomach cramps, vomiting, and nausea are typical symptoms of eating a toxin-contaminated food.
Noteworthy is that this staphylococcal food poisoning is not life-threatening.
Recommended articles
Staph aureus skin infection
Staphylococcus aureus is the main cause of;
Abscess and sycosis: An abscess develops when the body is infected with a bacterial infection. Abscesses can form anywhere on the body.
It is possible to develop two kinds of abscesses: one that develops under the skin and another that develops inside the body, inside an organ, or somewhere between organs.
Sycosis is the inflammation of hair follicles in the beard area.
Boils (furuncles and carbuncles): Boils are skin infections that start in hair follicles or oil glands. The area of infection typically turns red, and a lump appears.
Cellulitis: This is a dangerous Staphylococcus aureus infection of the skin. The infection can also spread to the blood, bones, lymph system, heart, or nervous system. These infections can lead to amputation, shock, or even death.
Folliculitis: Inflammation of the hair follicles causes folliculitis, a common skin condition.
Impetigo: Children and infants are usually affected by this highly contagious skin infection
Ecthyma: In this type of impetigo, sores penetrate deeper into the skin.
Folliculitis decalvans: a condition that causes baldness with scarring (cicatricial alopecia)
Dermatitis: In general, dermatitis refers to an irritation of the skin
Erysipelas Staphylococcus aureus
The main cause of erysipelas is a rare group of Streptococci. However, Staphylococcus aureus has been reported to be one of the causes.
These are skin infections often experienced by people with frequent skin injuries.
Some skin infections are also caused by toxins and they include,
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: Symptoms of the infection include peeling skin that looks like it has been burned or scalded by hot liquids.
Toxic shock syndrome: is a toxin-mediated acute life-threatening illness. It comes as a result of the release of toxins. High temperature and dizziness are signs of toxic shock syndrome.
Staphylococcal scarlatina: This condition is characterized by the absence of enanthems or exfoliation with occurrence in children and young adults.
Toxic shock syndrome is rare and life-threatening and may also be caused by toxins produced by group A streptococcus.
Staph aureus bacteremia
also known as SAB. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia is an infection in the bloodstream. These can either be community-acquired, healthcare-associated community-onset, or healthcare-associated hospital-onset.
This Staph aureus-caused disease is a serious one, and it therefore shouldn’t be taken lightly as it results in increased morbidity and mortality.
Recommended articles
Staphylococcus aureus lung infection
Staphylococcal pneumonia is a lung infection caused by Staph aureus. The infection causes the air sacs of the lung to fill with fluids and pus which eventually leads to cough, chills, fever, and trouble breathing.
Pneumonia is often community-acquired and is usually seen in patients who are recovering from influenza. However, it is noteworthy that pneumonia can also be caused by viruses, fungi, and other bacteria.
This is an airborne disease that is usually contagious. Another way of contracting it is through contact with contaminated objects.
Staph aureus endocarditis
This is a community-acquired disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This infection happens in the heart region thereby leading to the inflammation of the heart valves such as the aortic valves.
The damage to these valves causes them to be susceptible to the infection of this bacterium.
This is deadly heart disease with a mortality rate of 30-40%.
Staphylococcus aureus urinary tract infection
Staphylococcus is a leading cause of bacteriuria. Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in the urine, which can be either asymptomatic or symptomatic. Technically, this may not be regarded as among the staphylococcus aureus diseases.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is usually non-infectious. Bacteriuria is not fatal and is often found in people who have urinary tract catheterization.
Staphylococcus aureus meningitis
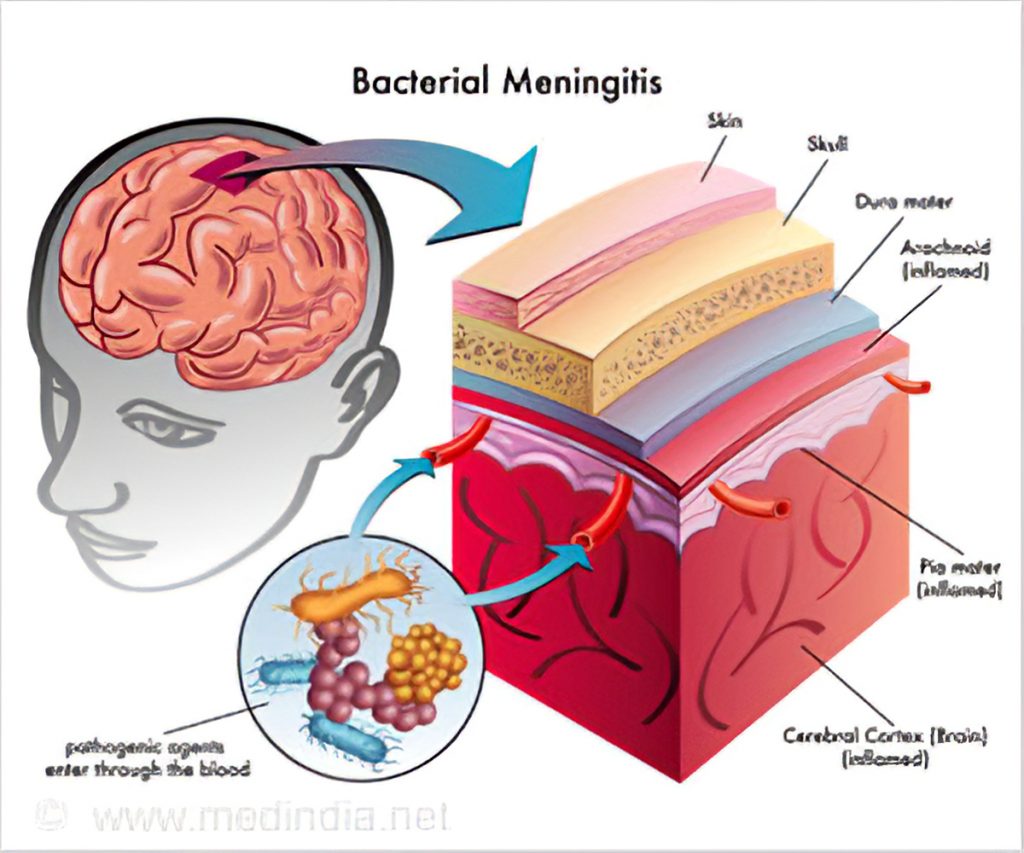
Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are the two major causes of meningitis. Meningitis is a bacterial infection of the meninges, a membrane covering the brain and spinal cord.
This infection is very fatal; however, it happens once in a blue moon. This disease can either be community-acquired or hospital-acquired.
According to Healthline, treatment is difficult and symptoms are almost non-existent.
Staphylococcus aureus eye infection
Staphylococcus aureus is a leading cause of infection of the eye. The site of infection is the conjunctiva, cornea, tear duct, eyelid, anterior and posterior chambers, and the vitreous chamber. Here is a list of Staphylococcus aureus diseases of the eye.
Keratitis is the inflammation of the cornea, whether due to an infection or not.
Endophthalmitis is an inflammation of intraocular fluids due to infection.
These two infections are fatal because they might lead to blindness.
Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids.
Conjunctivitis is the infection of the conjunctiva
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the nasolacrimal sac
Recommended articles
Staphylococcus aureus bone infection
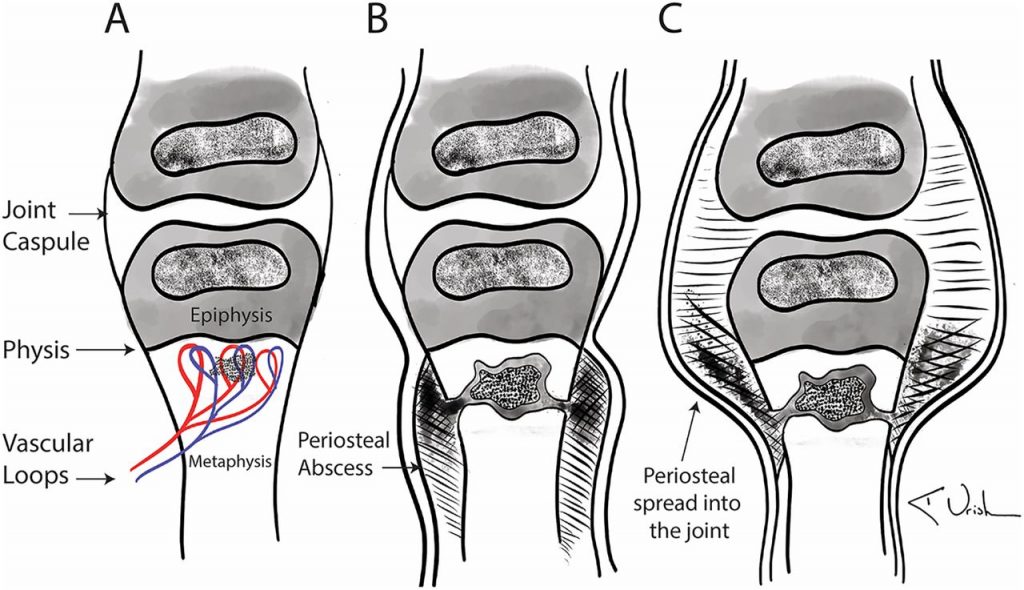
Osteomyelitis is a bone or skeleton infection caused by Staph aureus. This ailment is difficult to treat hence the mortality and morbidity rate is high.
Symptoms typically include a painful swelling of the bone marrow, which results in a cut-off of blood supply to the bone, causing the bone to whither.
According to Clevelandclinic, 2 to 5 out of every 10,000 people are affected with Osteomyelitis and it usually affects people of all ages and genders.
People with diabetes, bedsores, a broken bone, and sickle cell anemia are at a high risk of contracting this infection.
Staphylococcus aureus ear infection
A swimmer’s ear is a clear example of an ear infection caused by Staph aureus. However other bacteria such as Pseudomonas bacteria and fungi can cause this infection.
The signs of this ear infection include pain, muffled hearing, drainage of clear fluid, and fever.
Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion are variations.
Just like other infections, the Swimmer’s ear is a result of a tear of the ear skin while cleaning or scratching it.
Staph aureus septicemia
Do not confuse this with bacteremia. Bacteremia is simply the presence of bacteria in the blood while septicemia is the multiplication of bacteria in the blood thereby triggering sepsis.
Sepsis often times progresses to septic shock and it’s very deadly with a 50% death rate. This means that sepsis is dangerous and life-threatening.
Sepsis is not an airborne disease, nor is it a water-borne disease. It simply comes as a result of blood poisoning.
Slurred speech, nausea and vomiting, severe breathlessness, and diarrhea are some symptoms of sepsis or sepsis shock.
Other than Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and some types of Streptococcus are the lead bacteria that cause sepsis.
Staphylococcus aureus mastitis human
Mastitis is a breast infection in breastfeeding mothers. The breast tissues of a lactating mother are inflamed thereby leading to breast pain, redness and swelling.
However, it can also affect women who aren’t breastfeeding and men.
Noteworthy is that Staphylococcus aureus is responsible for the causes of chronic mastitis. The strain responsible for this is MRSA.
Staphylococcus aureus nasal infection
Staphylococcus aureus sinusitis is a disease of the nose. Sinusitis is the inflammation and swelling of the spaces inside your nose.
Symptoms include difficulty in breathing, stuffy nose, congestion, pain, headache, and swelling.
Sinusitis is of two types; acute and chronic. Staphylococcus aureus is responsible for chronic sinusitis.
Staphylococcus aureus kidney infection
Staphylococcus aureus can enter the kidney from the bloodstream thereby leading to Pyelonephritis, a disease of the kidney.
However, the major cause of about 90 percent of kidney infections is Escherichia Coli. Read more about Pyelonephritis here.
Staph aureus throat infection
A study has shown that methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) most commonly infects throats because its toxins cause inflammation, swelling, and infection.
Some observed signs and symptoms of staph infection in the throat are; pain in the throat, inflammation of the tonsils, excess mucus secretion, and nasal obstruction.
Staph aureus pharyngitis.
Recommended articles
Staphylococcus aureus surgical site infection
Staphylococcus aureus is the major bacterium in all surgical site infections. Surgical site infections are of three types: superficial incisional SSI, deep incisional SSI, and organ or space SSI.
Symptoms of surgical site infections include redness, fever, pain, warmth, and swelling.
Staphylococcus aureus diabetes
Lead author Patric Schlievert, Ph.D., and his University of Iowa colleagues investigated how the bacterium affects diabetes progression and discovered that chronic exposure to a toxin secreted by Staph aureus is a possible cause of type 2 diabetes.
Staphylococcus aureus nail infection
Paronychia (nail infection) usually results from bacteria. Most nail infections resolve with antibiotics. Paronychia typically does not cause serious health problems.
It occurs when Staph aureus penetrates the cuticle and the nail fold. Sometimes the infection lasts for a long time or recurs after treatment.
The symptoms of Paronychia include pain, swelling, pus, and tenderness around the nail. Paronychia is of two types: acute and chronic.
Conclusion
Here you have it: 35 Staphylococcus aureus diseases as seen in journals and peer reviews.
Let me know what you think in the comment box.
